
|
|
What is the purpose and function of the BIOS/UEFI?
Keywords:
overclocking, computer, settings, processor,
motherboard
Key Takeaway:
The BIOS is a special chip that resides on
your computer's motherboard.
Category Insights:
BEGINNER — This article is written to be accessible for newcomers to the
topic.
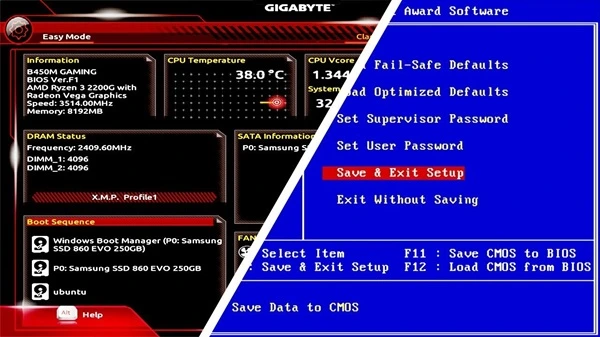
Basic Input Output System (BIOS)
The BIOS is a special chip that resides on your computer's motherboard. It’s programmed with special software called firmware that controls the basic functions of your computer. The BIOS keeps track of what hardware is inside your computer, including things like the processor (CPU), memory, hard drive, USB ports, fans, and even the system clock. The BIOS has default settings that are guaranteed to work. On basic motherboards, there might only be a few settings to change, using a text based interface. You can adjust the settings to customize how your computer works. For example: You can specify in the BIOS what harddrive should be used to boot the system, such as a CD or USB drive. If you make a mistake, you can choose the option to RESTORE DEFAULTS and your BIOS will revert to a working state.
Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
The UEFI is an enhanced / fancier version of the BIOS, providing support for
faster boot times, larger drives, and improved security. You will also find new features
such as TPM and Secure Boot. UEFI typically offers a more modern user interface with
numerous configuration options. There may be hundreds of settings on more advanced
systems. The terms BIOS and UEFI are sometimes used interchangeably.
P.O.S.T.
When you power on your computer, the BIOS runs first. Its the black screen
that appears BEFORE Windows or Linux starts. It performs a test called POST (Power-On
Self-Test) to make sure everything is working correctly. If something’s wrong, you’ll
see an error message. If everything passes, the BIOS checks the boot sector of the hard
drive to find the operating system (like Windows or Linux) and load it. The BIOS also
uses a small battery to keep the system clock running and remember your settings. This
whole process happens quickly, before your operating system fully takes over.
BIOS Updates
The firmware in the BIOS doesn’t usually need updates, but sometimes it’s
necessary to fix bugs, add new features, or support newer processors. It’s important to
only update the BIOS if you’re having problems, because updating it incorrectly could
seriously damage your computer. Interrupting the update could also cause problems,
so be careful if you decide to do it. Consult your manual or the manufacturers
website for instructions.
BIOS Flashback
Some motherboard have a feature called BIOS flashback. If a BIOS update
fails or becomes corrupted; you can use BIOS flashback. This will revert the BIOS back
to the original version from the factory. Consult the manual or manufacturers website
for instructions. Often times this feature can even be used without a processor
installed. Some boards will even have 2 copies of the BIOS on board so the user can
switch between them as needed.
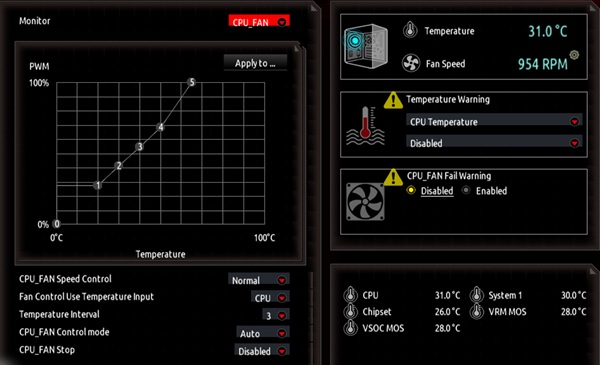
Fan Curves
High-quality motherboards provide users with the ability to configure
individual fans within the system, including CPU, case, and radiator fans. These fans
can be managed through either voltage control or PWM (Pulse Width Modulation). Gamers
may prefer a more aggressive cooling profile for improved performance, whereas office
users might prioritize quieter fan operation. Fan speeds are typically regulated by the
temperature sensors integrated into the motherboard and processor.
Processor Overclocking
Overclocking means adjusting the BIOS settings to make your CPU run faster
than usual. This is something gamers often do to boost performance and get a small
advantage over others. This assumes the processor and BIOS support the
overclocking feature. Processor overclocking is beyond the scope of this article.
Memory Overclocking
Your BIOS may have the option for memory overclocking This is typically
found on gaming computers. You can enable DOCP or XMP which will allow the memory to
perform faster. This assumes the memory in the computer supports the overclocking
feature. Memory overclocking is beyond the scope of this article.